An external Kriging python library can be applied using the Programmable Filter.
For example, if you want to use PyKrige (PyKrige — PyKrige 1.6.1 documentation), first, prepare the same version of the Python environment that ParaView uses, and install Pykrige on it. Then, copy:
-
Anaconda3/envs/pyKrige/Lib/site-packages/pykrige
-
Anaconda3/envs/pyKrige/Lib/site-packages/scipy
(This is an Anaconda example)
under (ParaView install folder)/bin/Lib/site-packages. After this preparation, start ParaView and apply a programmable filter to your geometry and observation points. Below is a concrete sample and its State file.
pyKrige.pvsm (567.3 KB)
The operation procedure is as follows.
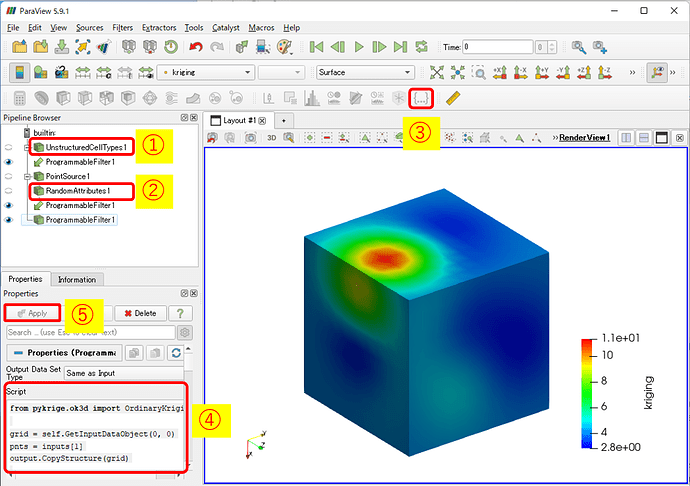
- Select the geometry data (UnstructuredCellTypes1) you want to interpolate or extrapolate in the Pipeline Browser.
- Continue to select the observation point data (RandomAttributes1) while holding down the Ctrl key.
- Then, start the Programmable Filter
- Type in the following in Script:
from pykrige.ok3d import OrdinaryKriging3D
grid = self.GetInputDataObject(0, 0)
pnts = inputs[1]
output.CopyStructure(grid)
k_psill = 10.0
k_range = 5.0
k_nugget = 0.002
ok3d = OrdinaryKriging3D(
pnts.Points[:,0], pnts.Points[:,1], pnts.Points[:,2], pnts.PointData['RandomPointScalars'],
variogram_model="gaussian", variogram_parameters ={'psill': k_psill, 'range': k_range, 'nugget': k_nugget}
#anisotropy_scaling_y=None, anisotropy_angle_z=None
)
k3d1, ss3d = ok3d.execute('points', output.Points[:,0], output.Points[:,1], output.Points[:,2])
output.PointData.append(k3d1, 'kriging')